As robotics technology advances, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and sophisticated sensing mechanisms are transforming how robots interact with their environments. Central to these developments is the concept of direct force control, which involves instructing robots through force-inclusive position feedback. This article explores the importance of direct force control, the role of AI in integrated force control, and predictive modeling. In addition, how these advancements drive the evolution of end effectors and enhance robotic performance across various applications is considered.
Direct Force Control
Direct force control enables robots to execute tasks with precision by incorporating force sensors that provide real-time force data. This feedback mechanism, known as force sensing, allows robots to adjust their movements and applied forces dynamically. Tactile sensing, a subset of force sensing, measures lower forces with greater accuracy by placing smaller sensors on critical parts of the robot, such as its fingertips. These sensors enable robots to perform delicate tasks requiring fine motor skills and precise control, significantly enhancing their functionality. Furthermore, direct force control improves robotic operations by continuously monitoring the force exerted by the end effector or robotic arm, preventing excessive force that could lead to equipment damage or personal injury.
AI and Predictive Modeling in Integrated Force Control
Building on the foundation of direct force control, AI advancements are significantly impacting the robotics field by enhancing how robots respond to their environment. AI technology is used for adaptive force control, allowing robots to learn from prior interactions and adjust the force they apply. This capability is particularly beneficial for intricate tasks like assembling small parts or handling fragile objects. Integrated force control leverages sensor fusion, where AI combines data from multiple sensors for real-time adjustments, ensuring precise force application. Using real-time operating systems like Xenomai and low-level programming languages such as C and C++ enable real-time responses with reduced latency.
By anticipating environmental changes, robots can adjust their force control to maintain stability and improve task performance. Reinforcement learning allows robots to continuously learn through trial and error in simulated environments, refining their responses to different scenarios and enhancing their adaptability.
Collaborative Robots and Autonomous Robots With Computer Vision
The advancements in AI and predictive modeling have paved the way for collaborative robots (cobots) and autonomous robots to operate more safely and efficiently. In collaborative robotics, where robots work alongside humans, AI dynamically adjusts force control without exerting unintended forces that could injure human workers. Computer vision, coupled with AI, enables autonomous robots to assess the force needed for picking or manipulating objects within parameters. AI algorithms optimize grasping positions and account for variations in object shape or weight. Object recognition algorithms help robots identify and classify objects, determining the best handling approach. Force sensors measure the applied force during interactions, feeding this data into the AI system to determine the required force for the intended task. AI decision-making processes analyze data from computer vision and force sensors to decide the optimal force, considering factors like weight, shape, and fragility. Machine learning algorithms allow robots to adapt their force control strategies based on feedback from previous interactions, improving their ability to handle different objects safely and efficiently. Integrating computer vision with AI enhances robots' ability to interact with their environment more adaptively, combining visual information with force sensing and intelligent decision-making.
Growth in End Effectors Driven by AI
The continuous evolution in AI and force control technologies is driving the growth of the robot end effector market. Over the past decade, the industrial robot market has witnessed substantial growth, driven by increasing automation demands across various industries. The anticipated growth of robot installations, with an estimated CAGR of 7% for the next two years (Figure 1), is fueled by the need for robots to handle more complex tasks. Traditional, single-purpose end effectors are becoming limiting, increasing the necessity for more versatile solutions that can adapt their grip strength, offer multi-articulated fingers for dexterity, and integrate advanced sensors for a richer understanding of objects. This demand for sophisticated end effectors is fueled by AI, and the development of these advanced tools empowers AI to tackle complex challenges, creating a mutually reinforcing cycle of innovation. Examples of AI-driven end effector innovation include universal grippers that adapt to various objects, soft robotic grippers for delicate manipulation, and AI-powered vision-guided grippers for precise grasping. As AI and robotics continue to evolve, we can expect more groundbreaking end effector designs, such as increased intelligence, improved designs for human-robot collaboration, and a focus on sustainable materials and energy efficiency.
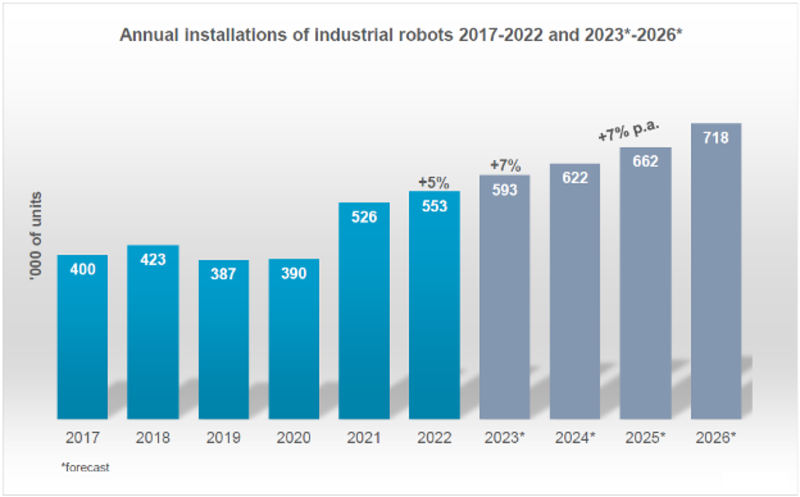
Figure 1: World Robotics Industrial Robots 2023: Annual Installations of Industrial Robots 2017-2022 and 2023-2026 (forecasted).
Accommodating Uncertainties
A key challenge in robotics is accommodating uncertainties, particularly in dynamic and unstructured environments. The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms significantly enhances this adaptability by enabling robots to learn from previous experiences and adjust their actions in real-time. Sensor fusion plays a vital role by combining data from various sensors, providing a comprehensive understanding of the environment and improving decision-making accuracy. Reinforcement learning allows robots to develop strategies through trial and error in simulated environments, refining their responses to variability. Predictive analysis with AI algorithms anticipates potential environmental changes, allowing robots to adjust their actions proactively. This approach minimizes the impact of sudden variations, enhancing operational stability despite environmental unpredictability.
Conclusion
The integration of AI and advanced force control technologies is revolutionizing the robotics field, enabling robots to perform complex, delicate, and dynamic tasks with greater precision and safety. As these technologies continue to evolve, the synergy between AI and sophisticated end effectors will further enhance robotic capabilities, paving the way for more innovative and efficient applications in various industries.
This article was written by Nina Anderson and Huan Gu.
Source
Müller, Christopher: World Robotics 2023 – Industrial Robots, IFR Statistical Department, VDMA Services GmbH, Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2023.






